Floater Thermostatic Steam Trap FTS 30-14
The thermostatic float steam trap, with a purely mechanical function, removes condensate and stagnant air from steam lines. This product is available in sizes from ½ inch to 1 inch, for pressures up to 16 bar and temperatures up to 220°C according to DIN standard.
Contact us for pricing and expert advice.
Thermostatic Floater Steam Trap | Price and Technical Specifications
The thermostatic float steam trap, with a purely mechanical function, removes condensate and stagnant air from steam lines. This product is available in sizes from ½ inch to 1 inch, for pressures up to 16 bar and temperatures up to 220°C according to DIN standard.
Floater Thermostatic Steam Trap: An efficient solution for steam systems
Steam Trap is one of the most critical components of the steam distribution network, playing a key role in improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs. Among them, the thermostatic float steam trap is a very reliable and widely used option due to its intelligent design and mechanical performance.
Application and operation of the float-thermostatic steam trap
The main function of this type of steam trap is to quickly and continuously drain condensate (distilled water), air and non-condensable gases from pipelines and heat exchangers, without losing live steam. This vital operation prevents water hammer and maximizes heat transfer.
Technical specifications and salient features
- Operating mechanism: A combination of a floater to drain condensate and a thermostat to release air and gases.
- **Sizing range:** From DN15 (½ inch) to DN25 (1 inch).
- Connection types: In two types: flange and threaded for flexibility in installation.
- Working parameters: Designed for a nominal pressure (PN) of 16 and a maximum working temperature of 220°C.
- Manufacturing standards: Manufactured in accordance with valid DIN standards, which guarantees high quality, durability and safety.
Why choose a float-thermostatic steam trap?
This steam trap model has excellent reliability due to the use of two independent mechanisms (float and thermostat). The continuous condensate discharge capability along with automatic air exhaust makes it an ideal choice for heat distribution units (heaters), dryers, heat exchangers (economizers) and many other applications.
How does the smart Floater Thermostatic Steam Trap mechanism work?
Understanding how a steam trap works is essential to selecting the best type and maintaining the efficiency of your steam systems. Thermostatic float steam traps offer reliable and efficient performance through a smart mechanical design. The operation of this device can be divided into two main parts:
- Condensate Drainage: The Main Task of the Floater
- In the initial state, when there is no condensation in the trap, the float ball is in its lowest position, causing the main valve to remain closed.
- As condensate enters the steam trap chamber, the liquid level gradually rises.
- This increase in surface area moves the floating ball upwards.
- The movement of the float through a mechanical lever system opens the ball or disc of the outlet valve gradually and proportionally to the amount of condensate collected.
- The great advantage of this mechanism: the gradual opening and closing of the valve prevents water hammer and, more importantly, prevents the loss of live steam. This system operates completely independently of sudden changes in line pressure.
2. Evacuation of air and non-compressible gases: Thermostatic Element function
- In addition to condensate, air and other non-compressible gases are always present in the system, the presence of which greatly reduces heat transfer efficiency.
- A thermostatic element (usually a capsule type) is installed at the top of the trap chamber.
- This element contracts upon contact with cold air, leaving a small valve open, which quickly releases trapped air from the system before startup.
- When hot steam reaches the trap, the thermostatic element expands and closes the air vent to prevent steam from escaping.
- Fail-safe function: If the float mechanism malfunctions for any reason, the thermostatic element senses the drop in temperature (caused by the accumulation of cold condensate) and opens the valve to prevent the system from completely blocking.
Fail-safe function: If the float mechanism malfunctions for any reason, the thermostatic element senses the drop in temperature (caused by the accumulation of cold condensate) and opens the valve to prevent the system from completely blocking.
This dual collaboration between the float and the thermostat makes this steam trap a very reliable and energy-efficient choice. This type of steam trap is especially ideal for applications where the amount of condensate produced is high and continuous, such as heat exchangers (heaters), coil sources, industrial dryers and baking ovens.
A comprehensive guide to installing a Floater Thermostatic Steam Trap
Thermostatic Floater Steam Trap Installation Instructions | How to Install Horizontally and Vertically Correctly | Complete Guide to Installing Thermostatic Floater Steam Trap Model FTS 30-14
Even more than choosing the right type, proper installation of a steam trap has a significant impact on energy efficiency, equipment life, and water hammer prevention in your steam system. This guide will help you install a thermostatic float steam trap in a completely correct and compliant manner.
1. Permitted steam trap installation directions
FTS 30-14 model steam traps have high installation flexibility and can be assembled in two main directions:
- Horizontal Installation:
- It is the most common and recommended installation method.
- The direction of steam and condensate flow can be from right to left or from left to right.
- In this case, the steam trap’s jar chamber (body) should be placed horizontally and parallel to the ground.
- Vertical Installation – Flow Down:
- In this method, the flow direction must be from top to bottom.
- This type of installation is usually used in limited spaces where horizontal installation is not possible.
2. Two vital points in any type of installation
Regardless of the installation direction, the following two rules must always be observed:
- Nameplate Arrow Direction Adjustment:
- There is a rating plate on the body of the steam trap with an arrow engraved on it.
- Once installed, this arrow must point downwards. This direction ensures the correct position of the internal mechanism (float and levers).
- Free and vertical movement of the Floater:
- The float mechanism inside the steam trap should be able to move up and down vertically without any obstruction. Avoid applying any pressure or bending to the connections that would restrict the float’s movement.
3. Adjustment and reassembly instructions
Our steam traps are usually assembled for horizontal installation by default. If you require vertical installation:
- Option 1 (recommended): Contact Technical Support at 02166800395. You can return the equipment to the company for assembly and reconfiguration based on your specific project needs.
- Option 2 (adjustment by the operator): If you have the necessary technical knowledge, you can refer to the manual and carefully follow the instructions in the “Maintenance and Repair” section, open the steam trap door, turn it, place the half-plate arrow in the correct direction (downward), and reassemble it.
4. Bypass Line Forecast
To facilitate troubleshooting, repair, and replacement of the steam trap without having to shut down the entire system, the installation of a bypass line is highly recommended.
- Benefits of bypass line:
- Possibility of separating the steam trap for service and maintenance
- Temporary system startup via bypass line in emergencies (with full compliance with safety considerations)
- Increase the reliability of the entire system
- Safety Tip: Good quality shut-off valves and a spare steam trap or similar valve must be used on the bypass line to prevent steam from escaping while the main trap is being serviced.
Final note: After installation, the first start-up should be done slowly and with gradual heating of the pipeline (with the help of air vents) to prevent thermal shock to the steam trap.
6- Technical specifications:
| size | Size | DN | 15 | 20 | 25 |
| IN | 1/2″ | 3/4″ | 1″ | ||
| How to connect | Connection Type | DIN | فلنجی | Flanged | |
| gear | Screwed (NPT) | ||||
| Working pressure difference | Working Press. Difference | Δp bar | 4.5, 10, 14 | ||
| Maximum nominal pressure | Max. Nominal Press. | PN16 | |||
| working temperature | Working Temp | (220 ˚C) | |||
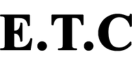



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.